3D Visualization for Daily Life: Everything You Need to Know

The Importance of 3D Rendering in Architecture Design
September 27, 2022"According to the compound annual growth rate (CAGR), the visualization and 3D rendering software market size was valued at $1.67 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $7.63 billion by 2027, growing at 22.62% from 2020 to 2027."

Overview
3D visualization has become an increasingly popular tool in daily life. From architectural design to video games, 3D visualization allows us to experience and interact with virtual environments in a way that is both realistic and immersive. In this blog post, we'll explore everything you need to know about 3D visualization and its use in everyday life.
First, let's define what 3D visualization is. Simply put, it's creating a digital representation of an object or environment that can be viewed in three dimensions. This can be done using various software programs and technologies, such as 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The result is a realistic, interactive 3D image or energy that can be seen on a computer or a virtual reality headset.
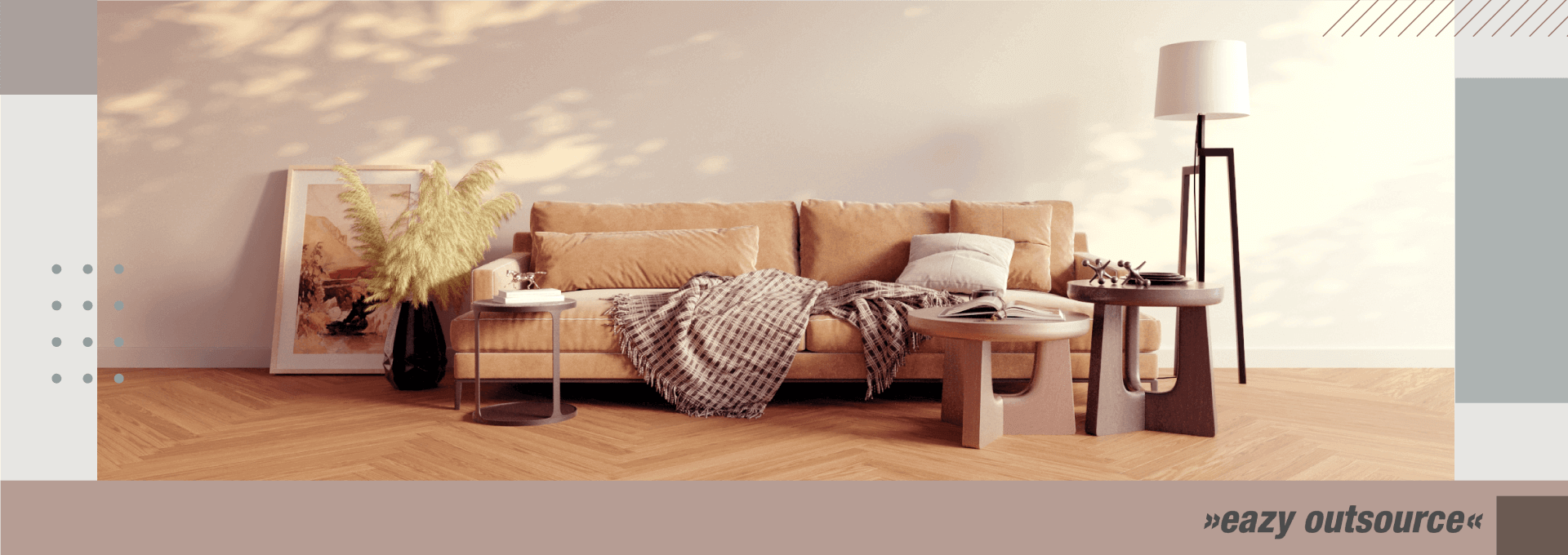
One of the most common uses of 3D visualization is in architecture and design. Architects and designers can use 3D visualization to create detailed models of buildings and other structures. This allows them to see how the finished product will look and make any necessary changes before construction begins. 3D visualization is also used to create virtual tours and walkthroughs of buildings, which can be a valuable way to market and show off properties.
Overall, 3D visualization is a powerful tool used in many fields and is becoming an increasingly important part of our daily lives. Whether you're an architect, designer, gamer, or just someone looking to experience something new, 3D visualization has something to offer. With the advancement of technology, it will be exciting to see how 3D visualization will continue to evolve and shape how we live, work, and play.
- What is 3D Visualization
- Where is 3D visualization used
- How Does 3d visualization work
- The necessity of 3D visualization
- Trends in 3D visualization for e-commerce
- Benefits of 3d visualization
- Begin your 3d visualization in 3 steps
- Conclusion
What is 3D visualization?
3D visualization has become an increasingly popular tool in daily life. From architectural design to video games, 3D visualization allows us to experience and interact with virtual environments in a way that is both realistic and immersive. In this blog post, we'll explore everything you need to know about 3D visualization and its use in everyday life.
First, let's define what 3D visualization is. Simply put, it's creating a digital representation of an object or environment that can be viewed in three dimensions. This can be done using various software programs and technologies, such as 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The result is a realistic, interactive 3D image or energy that can be seen on a computer or a virtual reality headset.
One of the most common uses of 3D visualization is in architecture and design. Architects and designers can use 3D visualization to create detailed models of buildings and other structures. This allows them to see how the finished product will look and make any necessary changes before construction begins. 3D visualization is also used to create virtual tours and walkthroughs of buildings, which can be a valuable way to market and show off properties.
Overall, 3D visualization is a powerful tool used in many fields and is becoming an increasingly important part of our daily lives. Whether you're an architect, designer, gamer, or just someone looking to experience something new, 3D visualization has something to offer. With the advancement of technology, it will be exciting to see how 3D visualization will continue to evolve and shape how we live, work, and play.
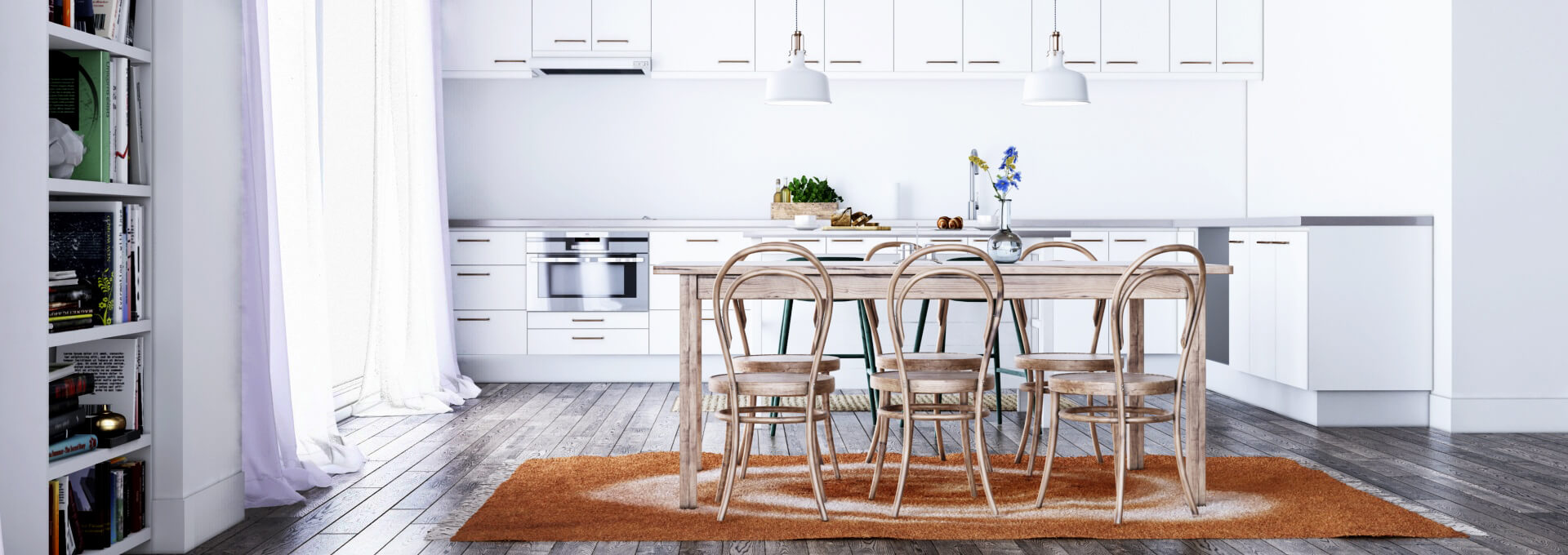

Where is 3D visualization used?
The benefit of three-dimensional modeling is that it can be applied to and help a wide range of industries. Businesses may use 3D projects to improve how they communicate with clients and provide them with an experience that is as good as being there. This technique is currently commonly used in the following fields:Architecture and design:
Architects and designers use 3D visualization to create detailed models of buildings, landscapes, and other structures. This allows them to see how the finished product will look and make any necessary changes before construction begins. 3D visualization is also used to make virtual tours and walkthroughs of buildings, which can be a useful way to market and show off properties.Gaming:
The gaming industry is another area where 3D visualization is heavily used. The gaming industry has become used to using 3D graphics and animation, which let players experience virtual worlds with a lot of detail and realism. 3D visualization is also being used in the field of entertainment, with companies like Disney creating virtual rides and attractions that allow visitors to experience their favorite movies and characters in a whole new way.How does 3D visualization work?
3D visualization is the process of creating a digital representation of an object or environment that can be viewed in three dimensions. This is done with the help of 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, as well as other software and technologies. The end result is a realistic, interactive 3D image or animation that can be seen on a computer or a virtual reality headset.The process of 3D visualization typically starts with 3D modeling, which is the creation of a digital representation of an object or environment. This is done using specialized software such as Autodesk 3ds Max, Maya, or Blender. Users of 3D modeling software can use shapes and forms to make detailed, accurate models of objects and environments.
Once the 3D model is complete, it can be animated to bring it to life. This is done by adding movement, such as the movement of a character or the rotation of an object. The animation can be done in a variety of ways, such as key frame animation or physics-based animation.
After the animation is done, the final step is rendering. This is the process of creating a final image or animation from the 3D model and animation. During the rendering process, lighting, textures, and other visual effects are added to the 3D model and animation data to make a realistic, detailed image or animation. This can be done using software such as Arnold, V-Ray, or Mental Ray.
Lastly, the final image or animation can be seen on a computer or virtual reality headset. This lets the user interact with the virtual world and explore it. 3D visualization can also be used for real-time rendering, which is used for interactive applications such as video games, virtual reality, and augmented reality. Real-time rendering uses a different approach to create the image, and it has to be optimized for fast performance to create the illusion of a 3D world that is interactive and responsive to the user.
In short, 3D visualization is a complicated process that uses different kinds of software and technologies to make 3D images and animations that are realistic, detailed, and interactive. It starts with 3D modeling, followed by animation and rendering to produce the final output that can be viewed and interacted with by the user.

The Necessity of 3D visualization
As it offers a wide range of advantages, visualization can be used for a variety of applications. So that you can see how beneficial 3D visualization may be, here are a few of them:Communication is enhanced through visualization
Visualization is mostly used to enhance visual communication and make sure that clients and artists are on the same page. Before a project reaches its final state, users may easily and swiftly preview how various components of it will appear.Cost-effective
The development of modern technology has made 3D visualization more affordable and easier to use. It is among the main reasons why visualization is such a well-liked marketing technique. When marketing your project, incorporating animations can help you save a significant amount of money.The simplicity of understanding various project options
Every project has a wide range of possibilities and concepts. It can be difficult for all project participants to communicate during these times. However, if everyone concerned can visualize how these various possibilities would appear, things get a lot simpler.Clear and accurate renderings
The most accessible and cost-effective way to show project ideas is probably to use a mix of real-world photos and 3D renderings. Whether it is related to architecture or not, VR technology is the future of every sector. Using virtual gadgets, you can view projects in a virtual reality environment from any angle or perspective you want. In the future, it will have amazing effects on construction projects.Benefits of 3D Visualization
E-commerce is made better by 3D visualization because it turns static product photography into a fun, dynamic, and easy way to show off products or services through graphics. Let's look at some of the advantages that 3D visualization software has to offer and how it works.Improves conversion and client retention
Before the invention of 3D visualization and rendering, going to a physical store was the only way to view an accurate portrayal of the product. At that time, the owner of the business did not know that optimizing the images would make the user experience better.It makes the buying process harder, and the clients are losing interest in online marketing. With 3D visualization, online shopping is now easier and more useful, which increases conversion rates and keeps customers coming back. A professional 3D visualization company helps brands make interactive models of their products that can be seen from all sides.Customers can modify and customize
The point of 3D visualization and rendering engines is to let customers change how products look and work to suit their needs. Customer happiness rises when businesses let customers see all of a product's key features and add their own touches. Companies use easy-to-use 3D product configurators to let customers customize their items by seeing them in 3D. Customers can easily change the texture, colors, features, or sizes of a product to make it fit their needs and tastes.It can create emotional connections.
E-commerce businesses must use emotional marketing along with efficient 3D visualization technologies when it comes to online sales.This is especially true for companies that sell expensive items, since buyers usually have higher standards given the prices they are willing to pay. This need is met by emotional marketing and 3D visualization, which show buyers photorealistic images of the product's main features and let them change them in real time to suit their tastes.Reduces costs and time.
It takes time to promote your products the traditional way with static images.You have to work with each object on its own and hire a photographer to take pictures of it from all angles. Also, if you really want great pictures, you will need to hire a professional photographer, which can be an expensive option. With 3D visualization, this arduous process can be avoided. With this method, you can get photos of your product that look real from any angle you want.
Begin your 3d visualization in 3 steps
Step 1: Select the item you wish to modify.
Whether it's the most-asked-about item or a texture with several layers, describing it is challenging.
Step 2: Shoot 3–5 photos or a video from different perspectives.
Don't spend money on a professional photographer; a picture taken with your phone will do the trick (or a few product links). Dimensions of the product, at least the most fundamental ones, will be required.
Step 3: Select the BEST service provider... Make sure the vendor you pick can provide scalable, high-quality services at a reasonable price. Make sure they meet your deadline if you need to convert more than 100 SKUs.
Conclusion:
The future of the world we live in depends on 3D visualization and 3D rendering. They have so many uses that it's easy to lose track of them. These fantastic techniques have applications across all industries. As technology changes, these techniques change along with it, giving the world more options. Both visualization and rendering have a part to play in the era of sustainability and smart cities.
FEBRUARY 10, 2023 | 15 MIN READ